Artículo de blog
- 23 de enero de 2025
- 8 minutos de lectura

- Kiara Saloojee
- DMARC Enthusiast
Reportes DMARC: Mejora la visibilidad de los entornos de correo electrónico

El Portal Sendmarc proporciona información útil sobre la seguridad del correo electrónico de tu organización a través de la Domain-based Message Authentication, Conformance, and Reporting(DMARC). Esta guía tratará sobre la configuración de DMARC, la navegación por el panel de control, el acceso a reportes detallados y la configuración de reportes automatizados para mejorar la gestión de la seguridad del correo electrónico de tu empresa.
Configuración de DMARC
Comienza por añadir el dominio de tu empresa a Sendmarc. Confirma que se han importado/aplicado los ajustes correctos y realiza los ajustes necesarios.
A continuación, hay una sección de "Configuración DNS" que muestra el registro del Sistema de Nombres de Dominio (DNS) necesario para habilitar la gestión DMARC, su estado de verificación y el registro DMARC sin procesar. Añade el registro de nombre canónico (CNAME) al DNS de tu organización para habilitar la delegación y verifica para validar el registro DNS.
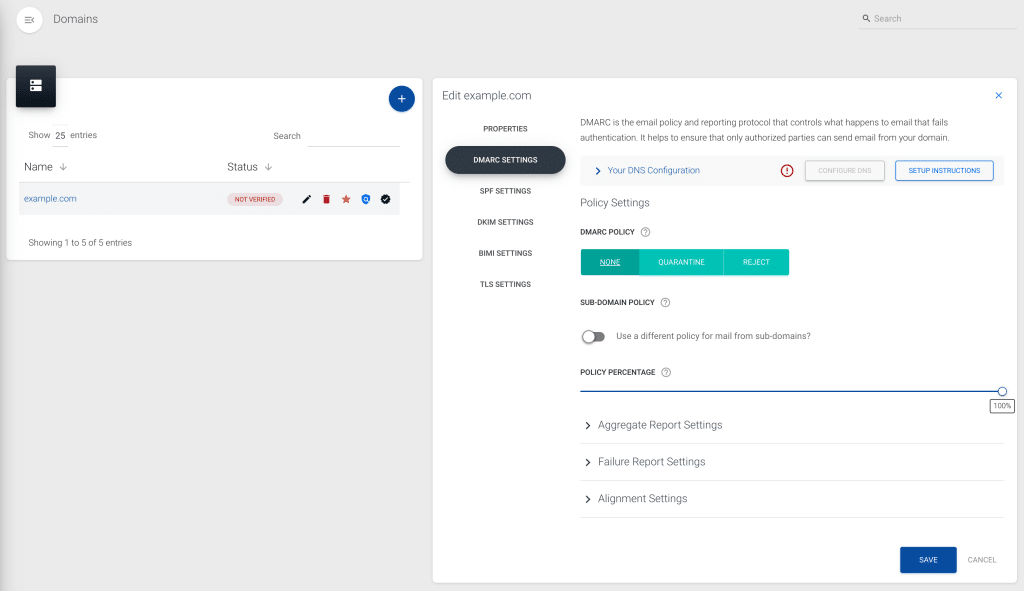
Estados de verificación
El estado de verificación revela si la gestión DMARC está activa:
- Verificado: El registro CNAME coincide y la delegación DMARC está habilitada.
- Verificación parcial: Se ha encontrado la dirección del reporte agregado o el registro bruto.
- No verificado: No se han encontrado registros coincidentes; es necesario volver a comprobarlo, especialmente en el caso de dominios nuevos.
Configuración de la política
Tras la verificación, configura la política DMARC del dominio:
Política DMARC
Las opciones son p=none (permitir todos los correos), p=quarantine (marcar correos sospechosos) y p=reject (bloquear correos no autenticados).
Recomendamos empezar con una política de p=none y pasar a p=quarantine y p=reject una vez que tu organización esté segura de que este cambio no afectará a la entrega del correo electrónico. Utiliza los datos DMARC para orientar la toma de decisiones.
Política de subdominios
Define cómo se gestionan los correos electrónicos de los subdominios, permitiéndoles copiar la política del dominio principal o tener la suya propia.
En general, recomendamos que esta política permanezca sin cambios (y que también se configure como p=reject lo antes posible). Si tu empresa tiene subdominios que requieren sus propias políticas DMARC , mejor crea registros DMARC individuales para ellos.
Porcentaje de la política
Establece el porcentaje de correos electrónicos a los que se aplicará la política DMARC. Esta etiqueta se eliminará pronto, por lo que es mejor no depender demasiado de ella durante laimplementación DMARC .
Reportes DMARC
Reportes agregados (RUA)
Los reportes agregados son resúmenes que proporcionan información sobre los correos electrónicos asociados al dominio de tu empresa, detallando el número de correos electrónicos enviados, los dominios remitentes y los estados de autenticación, e identificando posibles problemas.
Los reportes automatizados se gestionan en la "Configuración de reportes agregados" (Aggregate Report Settings) de la configuración de gestión del dominio. Aquí, tu organización puede establecer intervalos para la recepción de reportes (la mayoría de los proveedores sólo envían reportes una vez al día -así que piensa en esto como un intervalo solicitado en lugar de una instrucción) y añadir destinatarios adicionales (los receptores generalmente solo envían reportes a las dos primeras direcciones RUA).
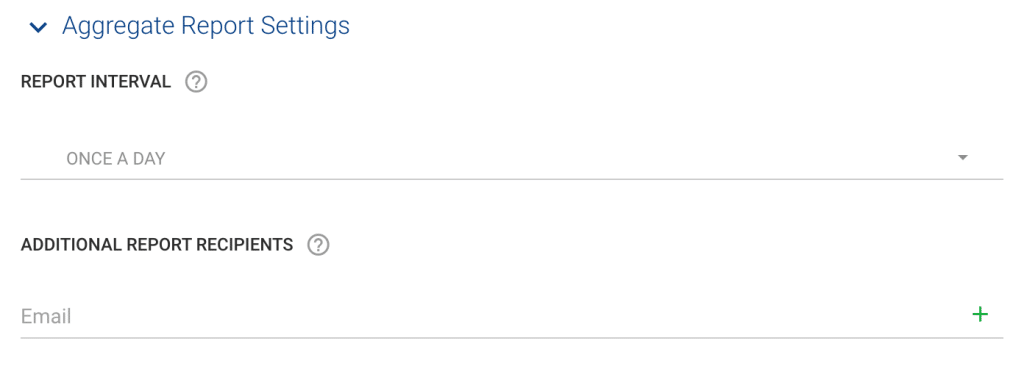
Reportes forenses (RUF)
Generados para correos electrónicos individuales que no superan la validación DMARC , estos reportes contienen información como las cabeceras de los correos electrónicos y el contenido del cuerpo, que resulta útil para solucionar problemas específicos. Se puede acceder a los reportes a través de varias vistas generales del panel, incluidos los reportes de errores.
Tu empresa puede activar o desactivar estos reportes y, si los activa, especificar los destinatarios y definir las condiciones en las que deben activarse.
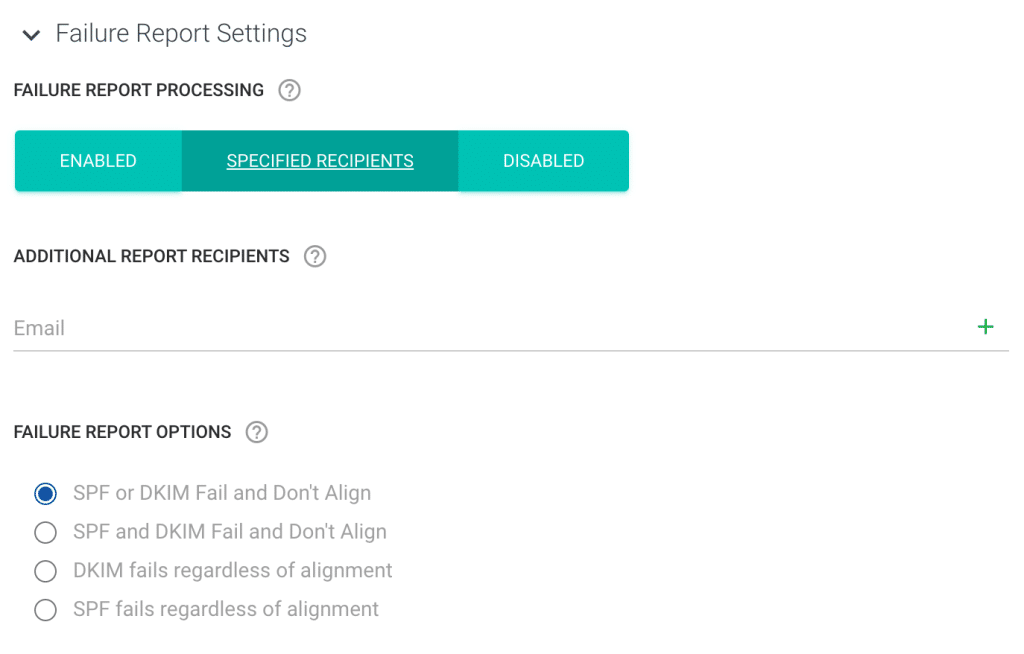
Ajustes de configuración
Determina el rigor de la alineación del origen del correo electrónico con las políticas del dominio utilizando los modos "Estricto" y "Relajado" (‘Strict’ and ‘Relaxed’) tanto para DKIM como para SPF.
Recomendamos utilizar "Relajado" (‘Relaxed’), ya que ofrece suficiente flexibilidad para enviar la mayoría de los tipos de correo electrónico.
Navegación por el panel de Sendmarc
El panel de Sendmarc ofrece una visión global de la seguridad del correo electrónico en todos los dominios de la cuenta de tu organización, con métricas clave.
Resumen tarjetas rápidas
- Ficha Dominios: Muestra estadísticas sobre dominios activos e inactivos y políticas DMARC aplicadas.
- Tarjeta de volumen: Muestra un desglose de los volúmenes de correo electrónico autorizados frente a los no autorizados dentro del periodo seleccionado, junto con los resultados de la autenticación.
- Tarjeta de remitentes: Categoriza los remitentes de correo electrónico, resaltando los cambios en función del número de remitentes marcados como autorizados.
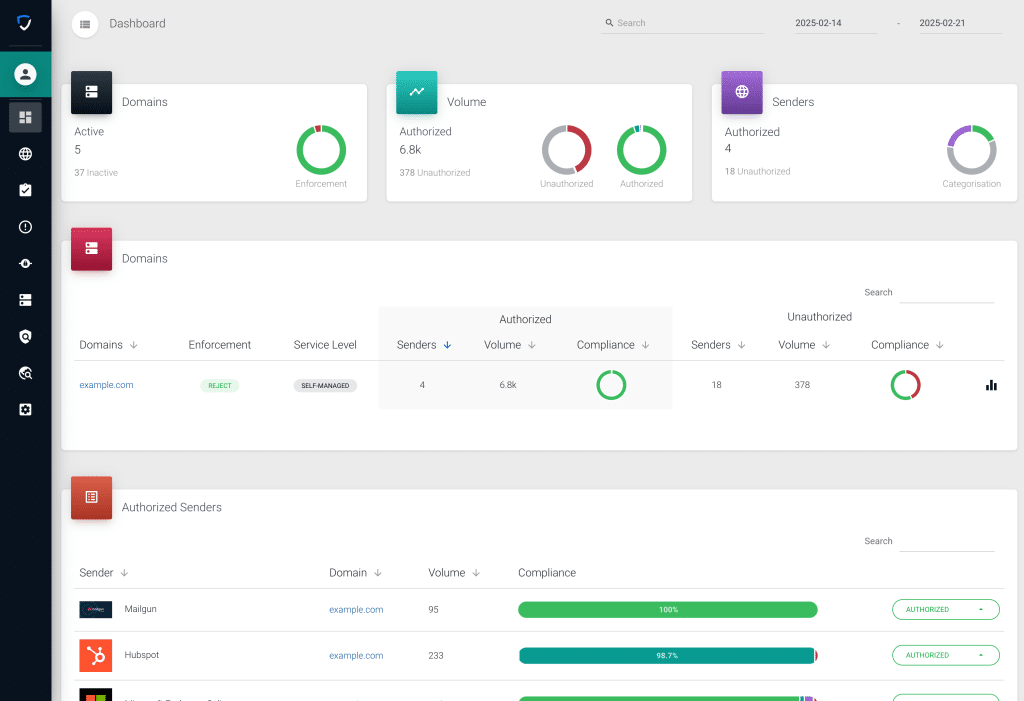
Fichas de desglose detalladas
- Dominios: Esta tarjeta ofrece una visión detallada de la información específica de cada dominio, como políticas de aplicación, niveles de servicio y listas de remitentes autorizados y no autorizados, con recuentos y volúmenes totales, acompañados de gráficos de cumplimiento.
- Remitentes autorizados: Se centra en los remitentes individuales agrupados como autorizados en todos los dominios, y ofrece detalles como nombres de dominio y remitentes, volúmenes de correo electrónico y niveles de cumplimiento.
- Cronología: Muestra las tasas de autenticación y fallos DMARC durante el periodo de tiempo seleccionado.
- Países de origen: Destaca los cinco principales países emisores con un mapamundi.
Cuadros de mando especializados
Los cuadros de mando especializados de Sendmarc se pueden encontrar navegando a la vista general de fuentes de correo electrónico. Aquí encontrarás los:
- Panel de cumplimiento: Ofrece resultados de autenticación DMARC para un dominio específico de la cuenta.
- Panel de entrega: Muestra las estadísticas de entrega utilizando los reportes de datos. Es diferente de los resultados de autenticación DMARC, porque muestra los casos en los que el sistema del destinatario ignoró DMARC y explica por qué.
- Panel de reputación: Supervisa la reputación IP en todos los dominios para tus remitentes autorizados.
- Panel de amenazas: Identifica amenazas a través de IPs para dominios para tus remitentes no autorizados.
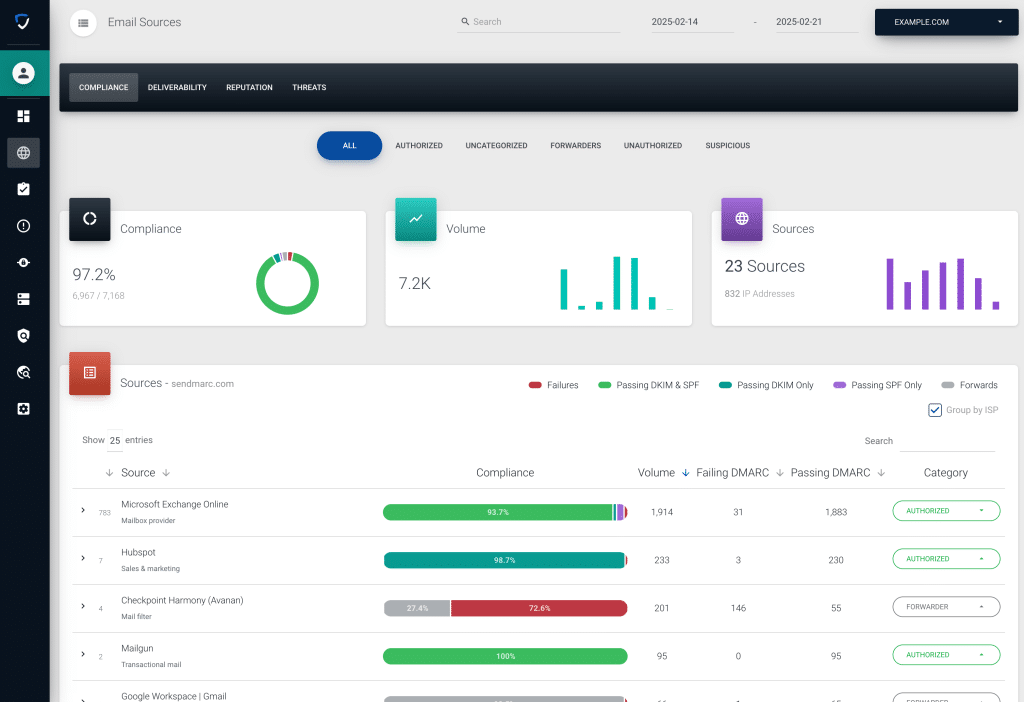
La plataforma Sendmarc proporciona potentes capacidades de supervisión y gestión, con actualizaciones en tiempo real y representaciones gráficas que ayudan a tomar decisiones informadas de forma eficaz. ¿Listo/a para tomar el control de la seguridad del correo electrónico de tu organización? Solicita una prueba gratuita.






