Page contents
DMARC authentication: Protect your domain and stop email fraud
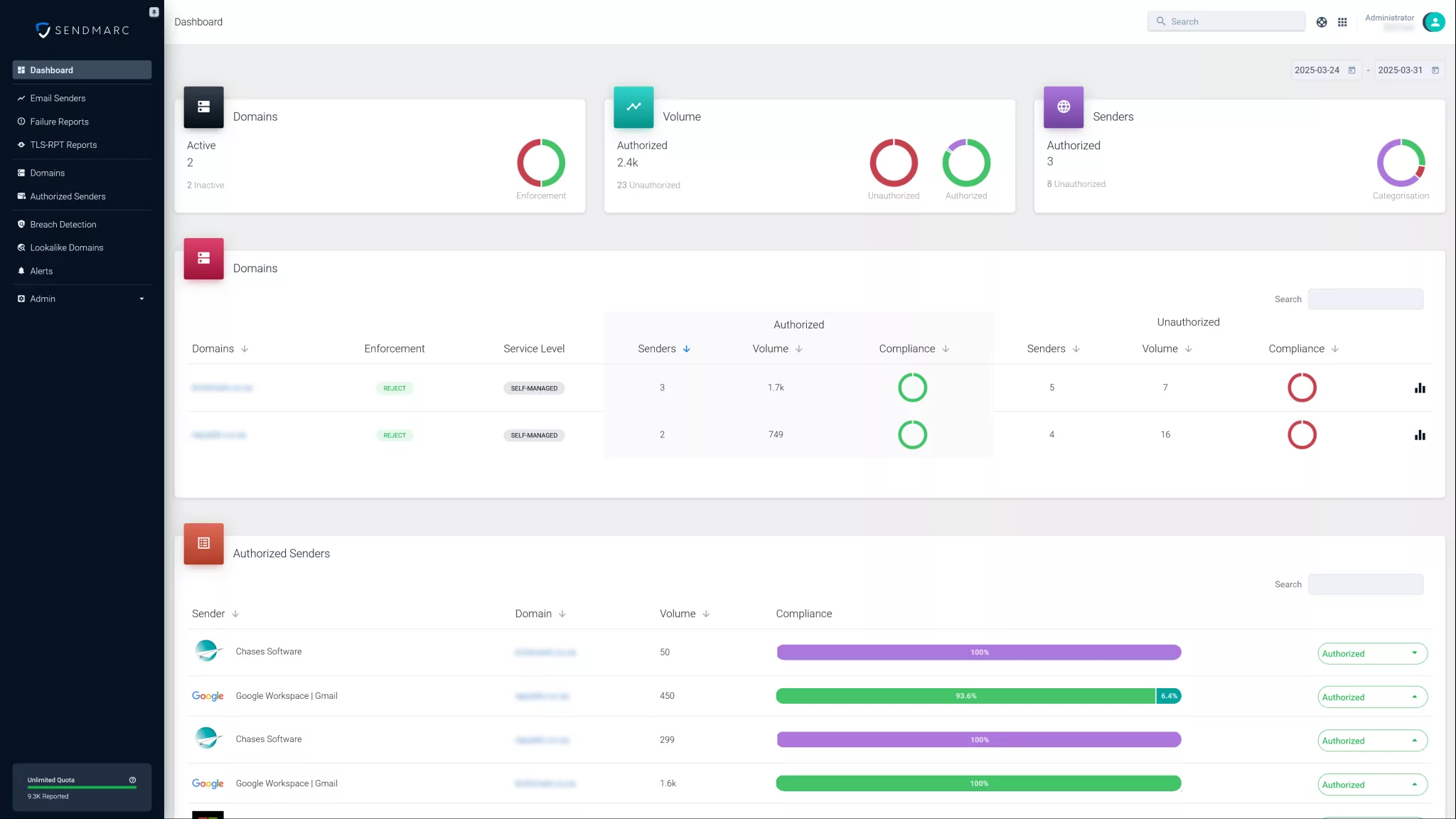
Sendmarc makes it easy to achieve DMARC authentication. Our platform helps you publish the correct record, monitor authentication results, and enforce policies that block fraudulent emails, so only trusted senders can use your domain.
Protect your domain. Improve deliverability. Authenticate with confidence.
What is DMARC authentication?
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) builds on two existing email authentication standards:
- Sender Policy Framework (SPF): Allows domain owners to specify which IP addresses are authorized to send emails on their behalf.
- DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM): Adds a digital signature to each email, which can be verified using a public key published in the domain’s DNS records.
DMARC connects to these two by:
- Instructing receiving email servers on how to handle messages that fail SPF and/or DKIM checks.
- Providing reports to domain owners for visibility into unauthorized email activity.
Together, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC create a layered email authentication strategy to prevent unauthorized use of your domain.
Why is DMARC authentication important?
Without DMARC authentication, your domain is exposed to email spoofing and phishing attacks. Cybercriminals can impersonate your brand to trick recipients into sharing sensitive data or downloading malware.
This can result in:
- Brand damage and reduced trust
- Financial losses due to fraud
- Lower email deliverability
Implementing DMARC email authentication:
- Protects your domain from unauthorized use
- Improves email deliverability and sender reputation
- Helps align with industry regulations and cybersecurity frameworks
Book a demo with Sendmarc to protect your domain from fraud and improve your email performance through DMARC authentication.
How does DMARC authentication work?
DMARC checks the alignment of the domain in the email’s ‘From’ header against the domains authenticated by SPF and DKIM:
- SPF check: Verifies if the sending server’s IP address is authorized to send emails on behalf of the domain.
- DKIM check: Validates the email’s digital signature against the public key published in the domain’s DNS record.
- Alignment check: Confirms that the domain in the ‘From’ header matches the domain authenticated by SPF and/or DKIM.
- Policy enforcement: Based on the DMARC policy published in the DNS, the receiving server decides whether to accept, quarantine, or reject the message.
- Reporting: DMARC provides aggregate and failure reports to the domain owner, allowing visibility into authentication results and potential abuse.
DMARC email authentication policies explained
DMARC policies define how receiving email servers should handle messages that fail authentication checks:
| Policy | Description | Use case |
|---|---|---|
none | Monitor only. No impact on delivery. Reports are still generated. | Initial deployment and visibility into email sources. |
quarantine | Suspicious emails are sent to Spam or Junk folders. | Intermediate enforcement while monitoring results. |
reject | Messages that fail DMARC are blocked outright. | Fully protect your domain with strict enforcement. |
Start with p=none to collect authentication data without affecting email flow. Once confident, gradually move to quarantine, then reject for stronger protection.
How to set up DMARC authentication
Requirements:
- Ensure SPF and DKIM are properly configured for all sending domains.
- Have access to your domain’s DNS management system.
Step-by-step setup
1. Create a DMARC DNS TXT record for your domain, including:
v=DMARC1– Protocol versionp=– Policy (none, quarantine, reject)rua=– Email address for aggregate reportsruf=– Email address for failure reports (optional)pct=– Percentage of emails subjected to policy (optional)
2. Publish the DMARC record in your domain’s DNS.
3. Set up a dedicated email address to receive DMARC reports for monitoring.
4. Test and verify your DMARC configuration using online tools.
5. Analyze incoming reports to identify legitimate and unauthorized senders.
6. Adjust your DMARC policy from none to quarantine, then reject based on insights gained from reports.
Troubleshooting DMARC authentication issues
DMARC authentication can fail for several common reasons:
- Incorrect or missing SPF or DKIM records
- Misalignment between the domain in the ‘From’ header and the domains authenticated by SPF and/or DKIM
- Forwarded emails that break SPF authentication
- DNS syntax errors or delays in record propagation
How to resolve DMARC authentication failures
If your domain is experiencing DMARC authentication failures, follow these steps:
- Verify SPF and DKIM records are correctly published and include all legitimate sending addresses.
- Ensure DKIM signatures are aligned with the domain in the ‘From’ header.
- Review DMARC reports to identify unauthorized or misconfigured email sources.
- Adjust your DMARC policy gradually, starting with monitoring to avoid blocking legitimate messages while configuring your settings.
Best practices for DMARC authentication
Implementing DMARC effectively requires a strategic approach.
Here are the key best practices:
- Monitor DMARC reports regularly to detect unauthorized activity and identify delivery issues.
- Start with a “none” policy to collect data without impacting email flow.
- Progress to “quarantine” and then “reject” as you gain visibility and control over your email sources.
- Maintain SPF and DKIM records by including all authorized email servers and third-party platforms.
- Educate your team on email authentication protocols and phishing risks to improve overall email security.
- Use trusted tools like Sendmarc to simplify DMARC implementation and policy management.
Ready to secure your domain?
Protect your domain from impersonation and improve your email deliverability with Sendmarc’s trusted DMARC authentication solution.
DMARC authentication FAQs
What is DMARC email authentication?
DMARC email authentication is a protocol that uses Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) to verify that emails are sent from authorized sources. DMARC authentication also instructs receiving email servers on how to handle messages that fail authentication checks.
How does DMARC authentication work?
DMARC authentication works by verifying SPF and DKIM results and checking if the domains authenticated by those protocols align with the domain in the email’s ‘From’ header. Based on the domain’s published DMARC policy, the receiving server will accept, quarantine, or reject the message if it fails authentication.
How do I pass DMARC verification?
To pass DMARC verification, your emails must pass either SPF or DKIM checks, and the domain authenticated by the protocol must align with the domain used in the ‘From’ header of the email.
How do I set up DMARC authentication?
To set up DMARC authentication, first configure SPF and DKIM for all your sending services. Then create and publish a DMARC record in your domain’s DNS. Finally, monitor the reports generated to make ongoing adjustments and improve your protection.
How do I fix a DMARC authentication failure?
To fix a DMARC authentication failure, verify that SPF and DKIM records are correctly configured and include all legitimate senders. Ensure the domains used for authentication align with the ‘From’ domain, and review DMARC reports to identify and address any issues. Update your DNS records as needed to resolve misconfigurations.
What does “DNS authentication DMARC fail” mean?
A “DNS authentication DMARC fail” message means that an email sent from your domain didn’t pass Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) checks. This typically happens when the email also fails Sender Policy Framework (SPF) and DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) validation, or when domain alignment is incorrect.